Decoding Wisconsin’s Climate: A Deep Dive into Radar Maps and Their Interpretation
Associated Articles: Decoding Wisconsin’s Climate: A Deep Dive into Radar Maps and Their Interpretation
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding Wisconsin’s Climate: A Deep Dive into Radar Maps and Their Interpretation. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding Wisconsin’s Climate: A Deep Dive into Radar Maps and Their Interpretation
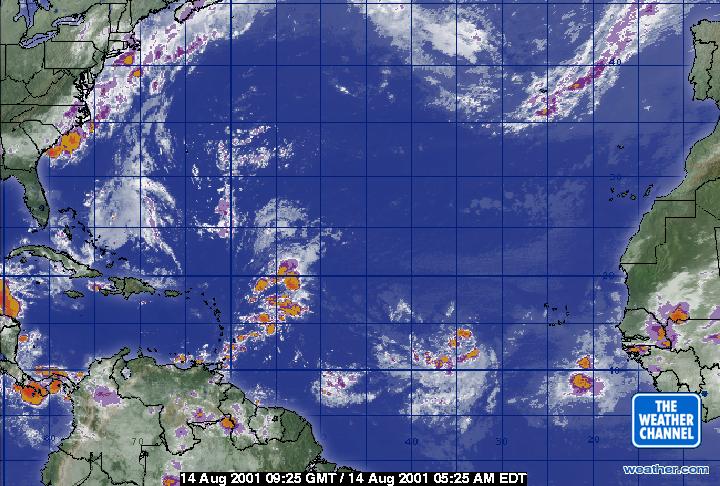
Wisconsin, with its numerous geography starting from the rolling hills of the Driftless Space to the huge expanse of Lake Michigan, experiences a large spectrum of climate phenomena. Understanding these climate patterns is essential for residents, companies, and emergency providers alike, and the important thing to this understanding lies in decoding Wisconsin’s radar maps. This text will delve into the intricacies of those maps, exploring their expertise, the info they characterize, the right way to interpret them successfully, and their significance in every day life and emergency preparedness.
Understanding the Expertise Behind Wisconsin’s Radar Maps:
The muse of Wisconsin’s climate radar community is a system of Doppler climate radars. These refined devices emit pulses of radio waves that bounce off precipitation (rain, snow, hail) and different atmospheric particles. By analyzing the time it takes for these pulses to return and the Doppler shift (a change in frequency brought on by the motion of the goal), the radar can decide the situation, depth, and motion of precipitation.
The Nationwide Climate Service (NWS) operates a number of Doppler radars strategically positioned throughout Wisconsin to offer complete protection. These radars are a part of the bigger NEXRAD (Subsequent Era Radar) community, a nationwide system that gives real-time climate knowledge. The info collected by these radars is then processed and displayed on numerous platforms, together with the NWS web site and quite a few climate apps.
Deciphering the Colours and Symbols on a Wisconsin Radar Map:
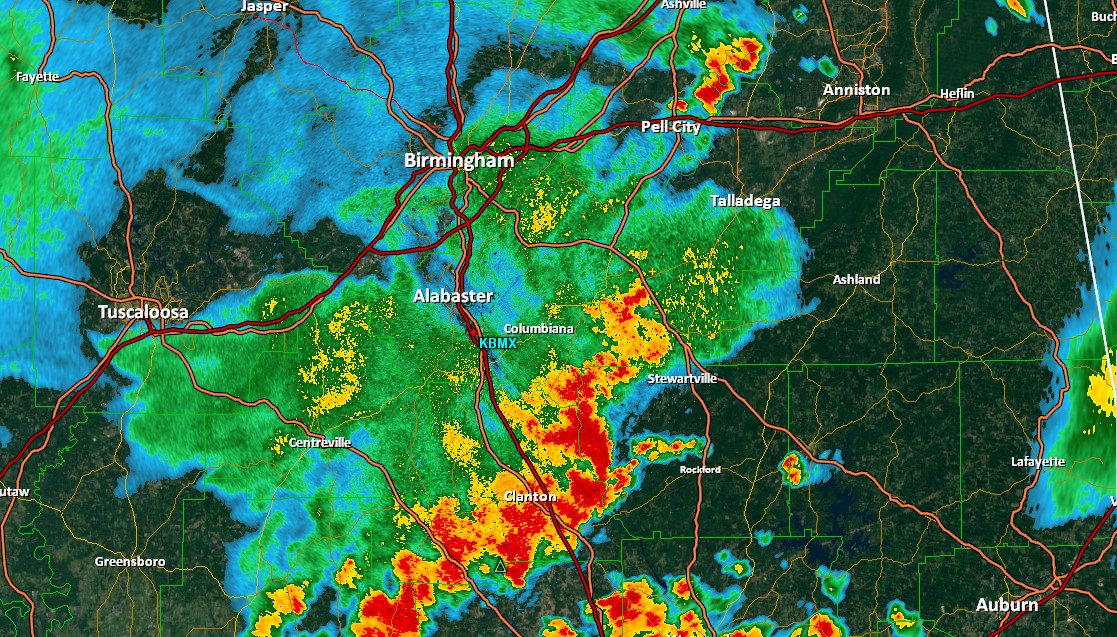
A typical Wisconsin radar map is a color-coded picture displaying the depth and kind of precipitation. The colour scale is standardized throughout the NEXRAD community, making it comparatively simple to interpret. Typically, shades of inexperienced characterize mild precipitation, progressing by way of yellow, orange, crimson, and purple to point more and more heavier precipitation. Purple usually signifies extraordinarily intense rainfall or hail.
Past the colour depth, a number of different symbols and options improve the map’s data content material:
-
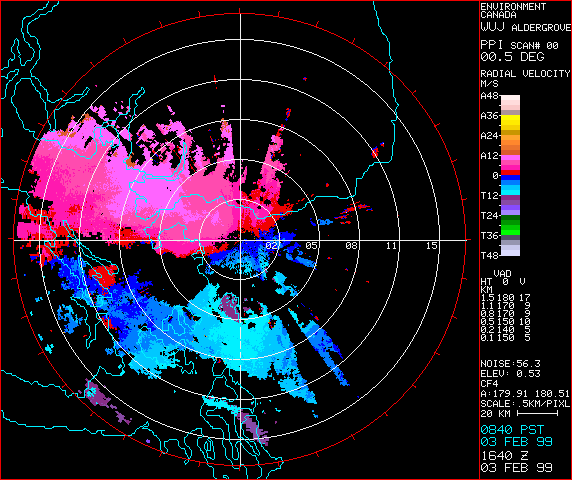
Velocity: Doppler radar additionally measures the radial velocity of precipitation – the velocity at which it is shifting in the direction of or away from the radar. That is usually displayed as an overlay on the precipitation depth map, utilizing completely different colours to characterize completely different velocities. Inexperienced usually signifies motion away from the radar, whereas crimson signifies motion in the direction of the radar. This data is essential for predicting the trail and timing of approaching storms.
-
Base Reflectivity: That is the elemental measurement displaying the depth of the returned radar sign, immediately associated to the quantity and dimension of precipitation particles. Larger reflectivity values point out heavier precipitation.
-
Storm Monitoring: Many radar maps incorporate storm monitoring options, displaying the expected path of serious climate techniques. These predictions are based mostly on the radar knowledge mixed with numerical climate fashions.
-
Hail: Some superior radar techniques can detect hail based mostly on the precise traits of the radar sign. These techniques could spotlight areas the place hail is prone to happen.
-
Tornadoes: Whereas radar can not immediately detect tornadoes, it might probably determine the atmospheric circumstances conducive to twister formation, akin to sturdy rotation (indicated by hook echoes) and vital updrafts.
The Significance of Radar Maps in Day by day Life and Emergency Preparedness:
Wisconsin’s radar maps are invaluable instruments for a variety of purposes:
-
Day by day Climate Forecasting: Meteorologists rely closely on radar knowledge to forecast every day climate circumstances, together with precipitation quantities, timing, and kind. This data is essential for planning every day actions, from commuting to out of doors occasions.
-
Extreme Climate Warnings: Radar knowledge is the spine of extreme climate warnings issued by the NWS. When radar detects indicators of extreme thunderstorms, tornadoes, or heavy snowfall, the NWS can subject well timed warnings to alert the general public, permitting for preparation and evacuation if vital.
-
Agriculture: Farmers use radar knowledge to observe precipitation patterns, serving to them make knowledgeable choices about irrigation, planting, and harvesting. Information of rainfall quantities and timing is important for crop administration.
-
Transportation: Radar knowledge is crucial for transportation planning and security. Freeway departments use radar to observe snowfall and ice accumulation, permitting them to plan for snow removing and highway closures. Airways use radar to trace storms and modify flight plans accordingly.
-
Emergency Administration: Throughout emergencies, akin to floods or blizzards, radar knowledge is essential for coordinating rescue efforts and assessing the extent of injury. Emergency responders use radar to trace the motion of storms and plan evacuation routes.
-
Hydrology: Radar knowledge gives essential data for hydrological modeling and flood forecasting. By monitoring rainfall quantities and patterns, hydrologists can predict river ranges and potential flooding.
Limitations of Radar Maps:
Whereas radar maps are extremely highly effective instruments, they do have limitations:
-
Floor Muddle: Radar alerts could be mirrored by non-meteorological targets, akin to buildings and timber, creating "floor litter" that may obscure precipitation alerts, particularly close to the radar website.
-
Beam Attenuation: Heavy precipitation can soak up and scatter radar alerts, resulting in underestimation of precipitation depth in very heavy storms.
-
Elevation Angle: Radar scans the environment at numerous elevation angles. Decrease elevation scans present higher ground-level element, whereas greater elevation scans present a broader view of the storm’s construction. Nevertheless, the radar beam’s top above the bottom varies with distance from the radar, resulting in potential uncertainties.
-
Knowledge Decision: Radar knowledge has a restricted decision, which means that it can not detect small-scale options akin to particular person microbursts or very localized hail.
Enhancing Radar Expertise and Knowledge Accessibility:
Steady enhancements in radar expertise are enhancing the accuracy and element of climate data. Advances in sign processing, knowledge assimilation methods, and the combination of different knowledge sources (akin to satellite tv for pc imagery and floor observations) are resulting in extra correct and well timed forecasts.
Moreover, the growing accessibility of radar knowledge by way of web sites, cell apps, and different platforms makes it simpler for the general public to entry and interpret this important data. This improved accessibility empowers people to make knowledgeable choices and take acceptable precautions throughout extreme climate occasions.
Conclusion:
Wisconsin’s radar maps are a important element of the state’s climate monitoring and forecasting system. Understanding the right way to interpret these maps – the colour scales, symbols, and limitations – is crucial for each every day life and emergency preparedness. By using the data offered by these maps, residents, companies, and emergency providers could make knowledgeable choices, enhancing security and minimizing the impression of extreme climate occasions. As radar expertise continues to advance, the accuracy and accessibility of this very important climate knowledge will solely enhance, additional strengthening Wisconsin’s skill to organize for and reply to the challenges posed by its variable local weather.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Decoding Wisconsin’s Climate: A Deep Dive into Radar Maps and Their Interpretation. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!