From Contour Traces to 3D Landscapes: Reworking Topographic Maps into Immersive Digital Terrain
Associated Articles: From Contour Traces to 3D Landscapes: Reworking Topographic Maps into Immersive Digital Terrain
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to From Contour Traces to 3D Landscapes: Reworking Topographic Maps into Immersive Digital Terrain. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
From Contour Traces to 3D Landscapes: Reworking Topographic Maps into Immersive Digital Terrain

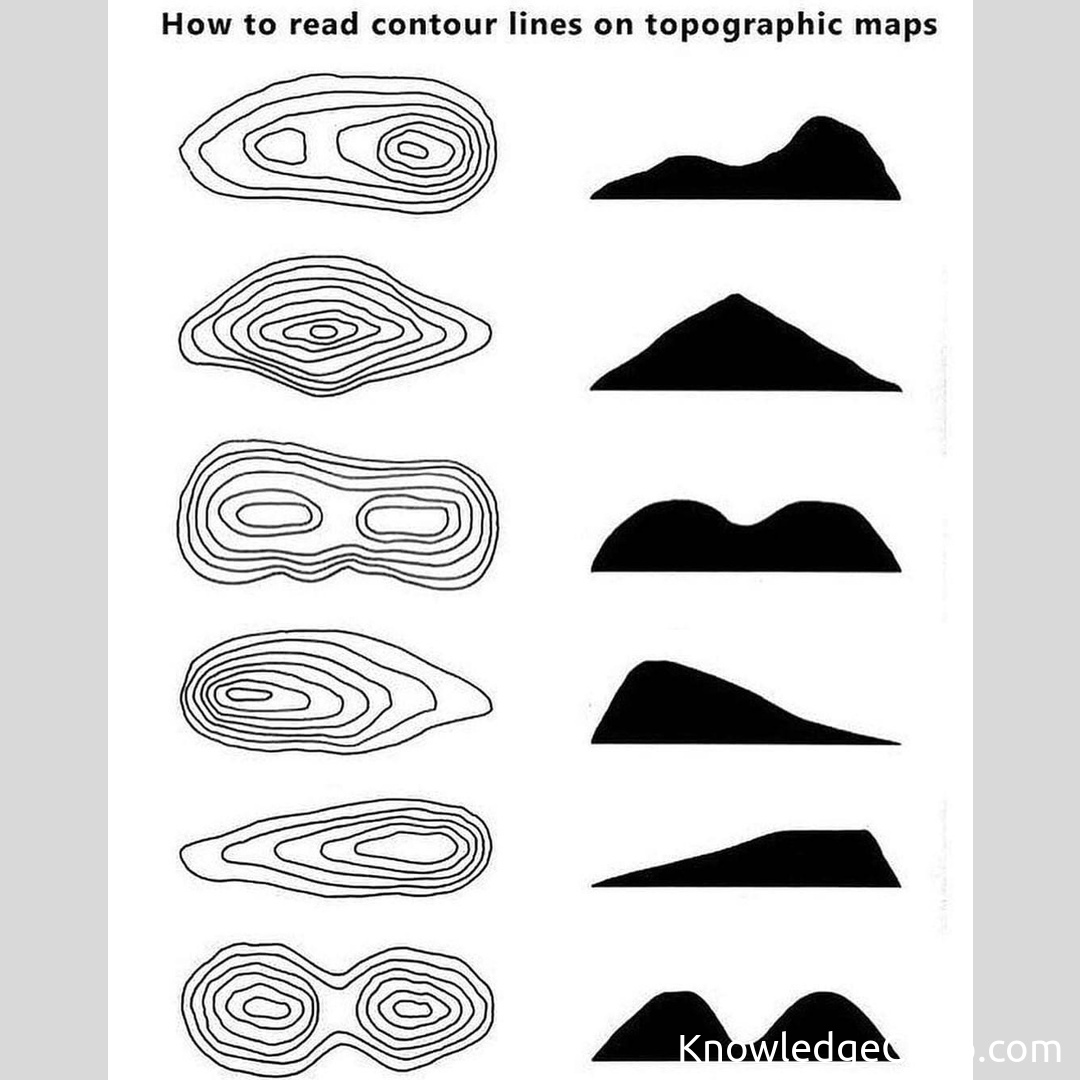
Topographic maps, with their intricate community of contour strains representing elevation, have lengthy served as important instruments for geographers, engineers, and outside fans. These two-dimensional representations, nonetheless, typically fall brief on the subject of visualizing the true three-dimensional nature of the terrain. Happily, developments in Geographic Data Programs (GIS) and 3D modeling software program have made it more and more simple to rework these static maps into dynamic, interactive, and visually beautiful 3D landscapes. This text explores the method of changing topographic maps to 3D fashions, analyzing the underlying methods, software program choices, and functions of this highly effective transformation.
Understanding the Basis: Topographic Map Information
The cornerstone of any profitable 3D mannequin derived from a topographic map is the standard of the supply information. A topographic map usually makes use of contour strains – strains connecting factors of equal elevation – to depict the terrain’s form. The nearer the contour strains are spaced, the steeper the slope. The vertical interval (the distinction in elevation between consecutive contour strains) is an important piece of knowledge, figuring out the accuracy and backbone of the ensuing 3D mannequin. Moreover, supplementary information, comparable to spot heights (particular person factors with recognized elevations) and breaklines (strains representing sharp adjustments in elevation, comparable to cliffs or ridges), considerably improve the accuracy and element of the 3D illustration.
The format of the topographic map information can be vital. Digital elevation fashions (DEMs) are more and more frequent, offering elevation information in a grid or level cloud format, making them perfect for direct import into 3D modeling software program. Raster information, comparable to scanned photographs of paper maps, require extra processing steps, typically involving picture evaluation and contour line extraction utilizing methods like vectorization. Vector information, which represents options as factors, strains, and polygons, affords better flexibility and precision, however might require extra handbook intervention to create a whole and correct DEM.
Strategies for Topographic Map to 3D Conversion:
A number of methods exist for remodeling topographic map information into 3D fashions, every with its personal strengths and weaknesses:
1. Direct Import and Interpolation: That is essentially the most simple technique, particularly when coping with DEMs. Software program packages like ArcGIS, QGIS, and International Mapper can immediately import DEM information and render it as a 3D floor. The software program makes use of interpolation methods, comparable to bilinear interpolation or kriging, to estimate elevations between information factors, making a clean and steady 3D floor. The accuracy of this technique relies upon closely on the density and high quality of the unique DEM information.
2. Contour Line Interpolation: For maps containing solely contour strains, the method entails interpolating the elevations between the strains. This may be achieved utilizing numerous algorithms, together with Delaunay triangulation, which creates a community of triangles connecting the contour strains, with elevation assigned to every vertex. This technique is computationally extra intensive than direct DEM import however affords a viable resolution when DEM information is unavailable.
3. TIN (Triangulated Irregular Community) Modeling: TIN fashions symbolize the terrain as a community of interconnected triangles, with every triangle representing a aspect of the 3D floor. This technique is especially helpful for areas with complicated topography, because it permits for better flexibility in representing sharp adjustments in elevation. Software program packages typically routinely generate TIN fashions from contour strains or DEM information.
4. Level Cloud Processing: Fashionable LiDAR (Mild Detection and Ranging) expertise generates huge level clouds containing hundreds of thousands of 3D coordinates with related elevation information. These level clouds may be immediately imported into 3D modeling software program and rendered as extremely detailed 3D fashions. Whereas indirectly derived from conventional topographic maps, LiDAR information typically enhances and enhances the accuracy of fashions created from maps.
Software program and Instruments for 3D Modeling:
A spread of software program packages facilitates the conversion of topographic maps into 3D fashions. The selection relies on components comparable to the kind of enter information, desired degree of element, and price range.
- ArcGIS: A strong and extensively used GIS software program package deal providing complete instruments for information processing, evaluation, and 3D visualization.
- QGIS: A free and open-source different to ArcGIS, offering most of the identical functionalities for 3D modeling.
- International Mapper: A specialised GIS software program specializing in 3D terrain modeling and evaluation.
- Blender: A free and open-source 3D creation suite able to importing and manipulating numerous information codecs, together with DEMs and level clouds.
- Autodesk 3ds Max: An expert-grade 3D modeling software program extensively used within the movie and animation trade, additionally able to dealing with large-scale terrain information.
Functions of 3D Topographic Fashions:
The functions of changing topographic maps to 3D fashions are huge and numerous:
- City Planning and Growth: 3D fashions present a sensible visualization of proposed developments, permitting planners to evaluate potential impacts on the encircling atmosphere and infrastructure.
- Civil Engineering and Development: Fashions support in web site evaluation, street design, and the planning of different infrastructure initiatives.
- Environmental Administration: 3D fashions help in visualizing and analyzing terrain options related to environmental research, comparable to erosion, flooding, and habitat mapping.
- Army and Defence: Fashions are used for terrain evaluation, mission planning, and coaching simulations.
- Training and Outreach: Interactive 3D fashions present participating and efficient instruments for instructing geography, geology, and different associated topics.
- Gaming and Digital Actuality: Lifelike 3D terrain fashions improve the immersive expertise in video video games and digital actuality functions.
- Flight Simulation: Correct terrain illustration is essential for sensible flight simulators.
Challenges and Concerns:
Whereas the method of changing topographic maps to 3D fashions has turn into more and more streamlined, a number of challenges stay:
- Information High quality: The accuracy of the 3D mannequin is immediately depending on the standard of the supply information. Incomplete, inaccurate, or low-resolution information will end in a much less correct and fewer visually interesting mannequin.
- Computational Assets: Processing giant datasets, significantly high-resolution DEMs or level clouds, may be computationally intensive, requiring highly effective {hardware}.
- Information Integration: Combining information from a number of sources, comparable to topographic maps, satellite tv for pc imagery, and LiDAR information, requires cautious consideration of information codecs and coordinate methods.
- Visualization and Rendering: Producing high-quality visualizations of complicated 3D fashions can require specialised software program and experience.
Conclusion:
The conversion of topographic maps to 3D fashions represents a big development in our potential to visualise and work together with the Earth’s floor. The methods described on this article, coupled with available software program instruments, empower customers throughout numerous disciplines to rework static two-dimensional maps into dynamic, interactive, and informative 3D landscapes. As expertise continues to advance, we will count on much more refined and environment friendly strategies for producing more and more sensible and detailed 3D terrain fashions, additional increasing the functions of this highly effective expertise. The power to visualise the three-dimensional nature of the earth’s floor is not confined to specialised professionals; it’s now accessible to a wider viewers, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of our planet’s complicated topography.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights into From Contour Traces to 3D Landscapes: Reworking Topographic Maps into Immersive Digital Terrain. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!