Mapping the Way forward for Farming: The Rise of the Farmer Map and its Affect on Agricultural Sustainability
Associated Articles: Mapping the Way forward for Farming: The Rise of the Farmer Map and its Affect on Agricultural Sustainability
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Mapping the Way forward for Farming: The Rise of the Farmer Map and its Affect on Agricultural Sustainability. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the Way forward for Farming: The Rise of the Farmer Map and its Affect on Agricultural Sustainability

The worldwide meals system faces unprecedented challenges. Local weather change, inhabitants development, and dwindling sources demand progressive options to make sure meals safety for a rising inhabitants. On the coronary heart of this problem lies the farmer, the person chargeable for producing the meals that sustains us. Empowering farmers with the appropriate instruments and data is essential, and on this context, the "farmer map" – a broad time period encompassing a variety of geospatial applied sciences and data-driven platforms – is rising as a robust instrument for agricultural transformation. This text will discover the assorted sides of farmer maps, their capabilities, limitations, and their essential function in reaching sustainable and resilient agricultural techniques.
What’s a Farmer Map?
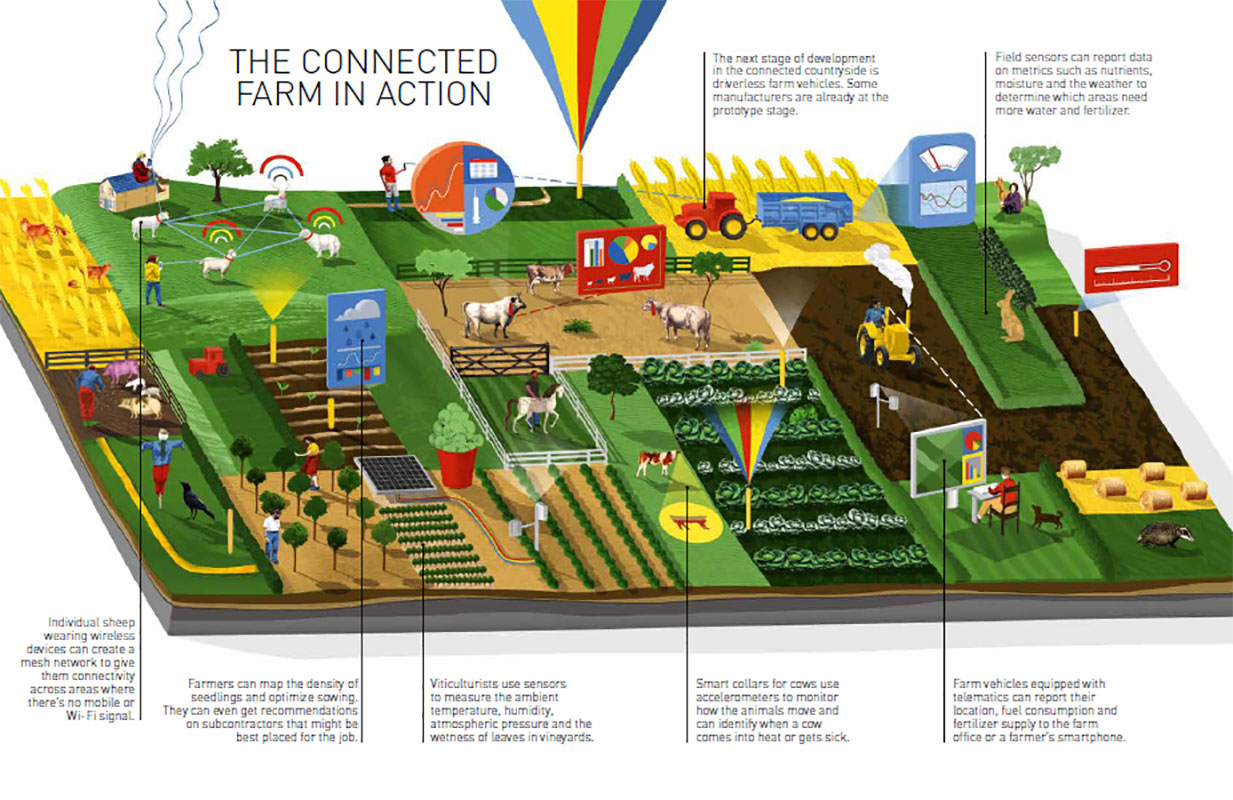
A farmer map, in its easiest kind, is a visible illustration of agricultural land, incorporating numerous layers of information related to farming practices. Nonetheless, the time period encompasses a much wider spectrum of applied sciences and functions. It could vary from easy, manually created maps displaying area boundaries and crop varieties, to classy, digitally built-in platforms that leverage satellite tv for pc imagery, sensor knowledge, climate forecasts, and market data to offer farmers with real-time insights and decision-support instruments. These superior platforms typically combine with Geographic Info Techniques (GIS) and precision agriculture applied sciences, providing a complete view of the farm and its environment.
Key Options and Capabilities of Superior Farmer Maps:
Fashionable farmer maps are way over static representations of land. Their capabilities embody:
-
Precision Mapping of Fields: Correct delineation of area boundaries, incorporating variations in topography, soil varieties, and different related elements. This enables for focused utility of inputs like fertilizers and pesticides, minimizing waste and environmental impression.
-
Soil Mapping and Evaluation: Integration of soil knowledge derived from laboratory evaluation, distant sensing, and historic information. This permits farmers to grasp soil nutrient ranges, pH, and different properties, optimizing fertilization methods and enhancing crop yields.
-
Crop Monitoring and Yield Prediction: Using satellite tv for pc imagery, drones, and sensor networks to observe crop well being, development phases, and potential yield. Early detection of stress elements like drought or illness permits for well timed interventions, stopping important yield losses.
-
Irrigation Administration: Integration of information on soil moisture, rainfall, and evapotranspiration to optimize irrigation schedules, conserving water sources and enhancing water-use effectivity.
-
Pest and Illness Administration: Detection of pest and illness outbreaks via picture evaluation and sensor knowledge, enabling focused utility of management measures, minimizing pesticide use and lowering the danger of resistance.
-
Climate Forecasting and Local weather Danger Evaluation: Entry to hyperlocal climate forecasts and local weather change projections, permitting farmers to adapt their planting schedules and farming practices to mitigate climate-related dangers.
-
Market Info and Worth Evaluation: Integration of market knowledge on crop costs, demand, and provide chains, enabling farmers to make knowledgeable choices concerning planting, harvesting, and advertising and marketing their produce.
-
Farm Administration and Document Preserving: Digital platforms typically combine farm administration instruments, enabling farmers to trace inputs, bills, yields, and different related knowledge, enhancing farm profitability and effectivity.
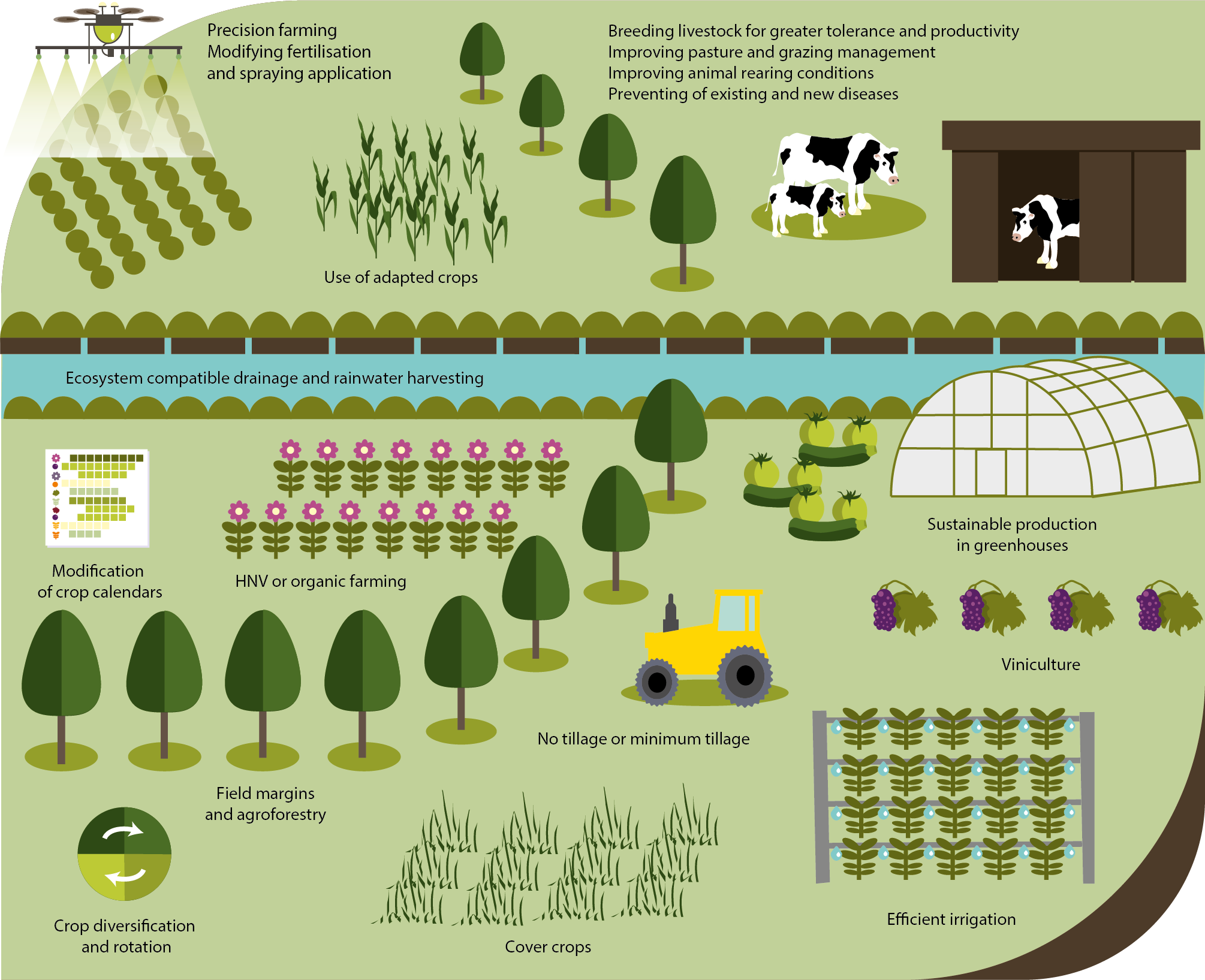
Advantages of Farmer Maps for Sustainable Agriculture:
The adoption of farmer maps presents important advantages for sustainable agricultural practices:
-
Elevated Productiveness and Effectivity: Optimized useful resource utilization, improved crop yields, and decreased enter prices contribute to elevated farm profitability.
-
Lowered Environmental Affect: Focused utility of inputs minimizes air pollution, conserves water sources, and reduces greenhouse gasoline emissions.
-
Enhanced Resilience to Local weather Change: Improved understanding of local weather dangers and entry to well timed climate data allow farmers to adapt their practices and mitigate the impacts of local weather variability.
-
Improved Meals Safety: Elevated productiveness and resilience contribute to enhanced meals safety at each native and world ranges.
-
Empowerment of Farmers: Entry to data and decision-support instruments empowers farmers to make knowledgeable decisions and enhance their livelihoods.
Challenges and Limitations of Farmer Maps:
Regardless of their potential, farmer maps face a number of challenges:
-
Knowledge Availability and Accessibility: Entry to high-quality, dependable knowledge is essential however might be restricted in lots of areas, significantly in creating nations. Knowledge infrastructure, web connectivity, and digital literacy are important limitations.
-
Price and Technological Experience: The price of buying and sustaining superior farmer map applied sciences might be prohibitive for a lot of smallholder farmers. Technical experience can be required for efficient use and interpretation of the information.
-
Knowledge Privateness and Safety: Issues concerning the privateness and safety of farm knowledge should be addressed to make sure accountable knowledge administration and forestall misuse.
-
Integration and Interoperability: Completely different farmer map platforms and applied sciences will not be simply built-in, hindering seamless knowledge alternate and evaluation.
-
Capability Constructing and Coaching: Efficient implementation of farmer maps requires enough coaching and capability constructing for farmers and extension employees.
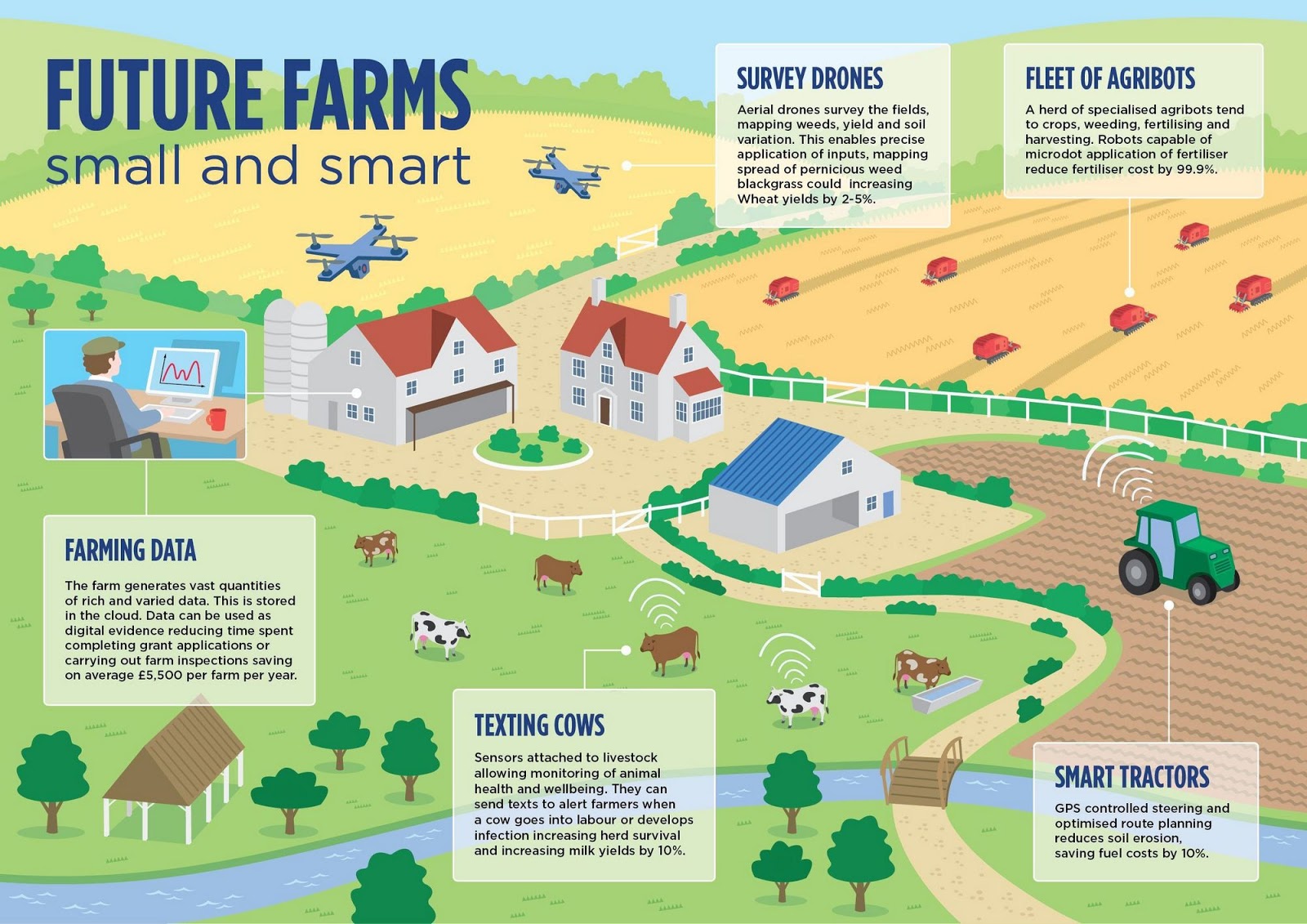
The Way forward for Farmer Maps:
The way forward for farmer maps lies of their continued evolution and integration with different rising applied sciences. Key tendencies embody:
-
Synthetic Intelligence (AI) and Machine Studying (ML): AI and ML algorithms can improve the evaluation of geospatial knowledge, offering extra correct predictions and suggestions for farmers.
-
Web of Issues (IoT): Integration of IoT sensors and units will present much more granular knowledge on farm circumstances, enabling real-time monitoring and management.
-
Blockchain Expertise: Blockchain can improve knowledge safety and traceability, enhancing transparency and belief throughout the agricultural provide chain.
-
Open-Supply Platforms and Collaboration: Improvement of open-source farmer map platforms can promote wider accessibility and encourage collaboration amongst stakeholders.
-
Deal with Smallholder Farmers: Efforts to tailor farmer map applied sciences and help providers to the particular wants of smallholder farmers are essential for reaching inclusive and sustainable agricultural growth.
Conclusion:
Farmer maps characterize a big development in agricultural expertise, providing the potential to rework farming practices and contribute to a extra sustainable and resilient meals system. Whereas challenges stay when it comes to knowledge accessibility, price, and capability constructing, the advantages of those applied sciences are plain. By addressing the constraints and fostering collaboration amongst stakeholders, we are able to harness the ability of farmer maps to empower farmers, enhance meals safety, and shield our planet’s sources for future generations. The way forward for farming is more and more intertwined with the flexibility to successfully map, monitor, and handle our agricultural landscapes, making the farmer map not only a software, however a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Mapping the Way forward for Farming: The Rise of the Farmer Map and its Affect on Agricultural Sustainability. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!