The Caspian Sea: A Landlocked Big on the World Map
Associated Articles: The Caspian Sea: A Landlocked Big on the World Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to The Caspian Sea: A Landlocked Big on the World Map. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Caspian Sea: A Landlocked Big on the World Map

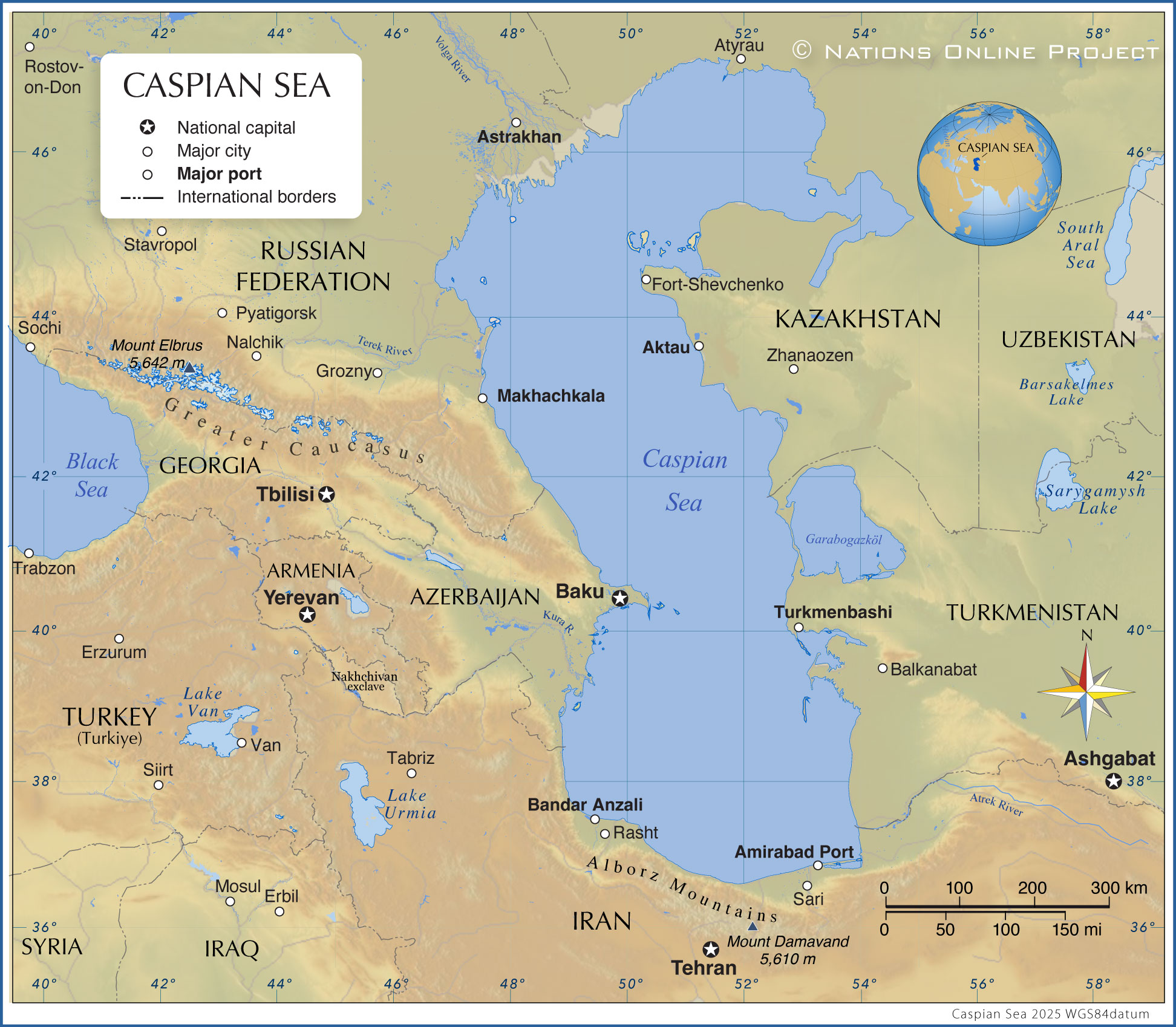
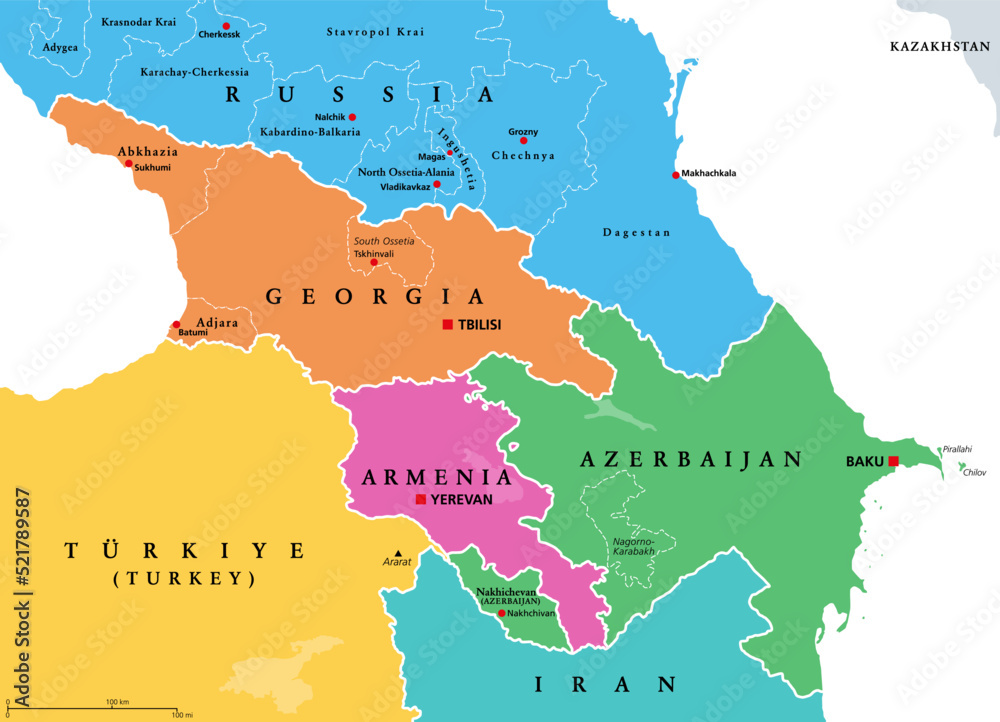
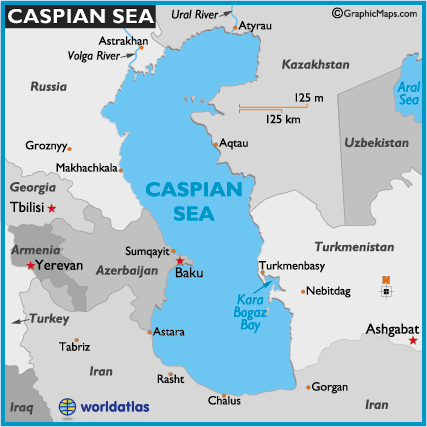
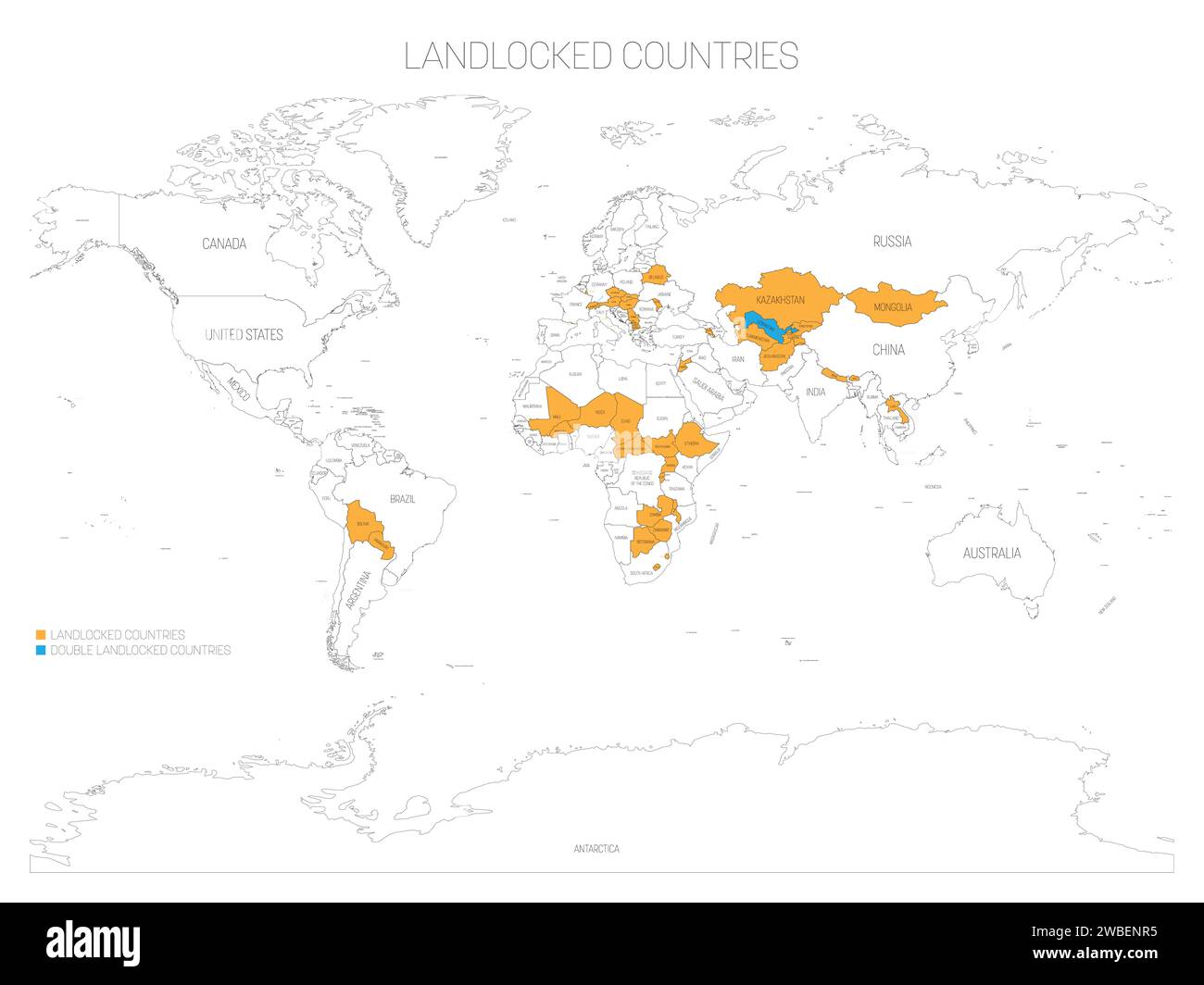
The Caspian Sea, the world’s largest inland physique of water, holds a singular place on the worldwide map. Neither a lake nor a sea within the strictest geographical sense, its huge expanse and sophisticated ecosystem make it an enchanting and very important geographical characteristic with important geopolitical and environmental implications. Its location on the crossroads of Europe and Asia, bordering 5 nations – Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan – underscores its historic and modern significance.
Geographical Context and Dimensions:
Located between 36° and 47° North latitude and 46° and 55° East longitude, the Caspian Sea is a very large inland water physique. Its floor space fluctuates relying on water ranges, but it surely typically covers an space of roughly 371,000 sq. kilometers (143,000 sq. miles), surpassing the mixed space of many nations. Its most size is roughly 1,200 kilometers (750 miles), and its most width reaches roughly 435 kilometers (270 miles). The ocean’s depth varies considerably, with a most depth of 1,025 meters (3,363 ft) in its southern basin, whereas the northern half is significantly shallower. This variation in depth contributes to the various habitats and ecosystems discovered inside the Caspian.
The Caspian Sea’s distinctive character lies in its endorheic nature – it has no outlet to the ocean. Which means the water degree is primarily regulated by the stability between influx from rivers and evaporation. Over the previous century, the water degree has fluctuated significantly, influenced by local weather change, dam building on its inflowing rivers, and variations in precipitation patterns. These fluctuations have important implications for the encircling ecosystems and human actions.
Hydrology and Ecology:
A number of main rivers feed into the Caspian Sea, most notably the Volga, Ural, Kura, and Emba rivers. The Volga, originating in Russia, is the most important river flowing into the Caspian, contributing a considerable portion of its freshwater influx. These rivers carry important quantities of sediment and vitamins, shaping the ocean’s ecology and influencing its salinity ranges.
The Caspian Sea’s salinity varies significantly throughout its completely different areas. The northern half, being shallower and receiving extra freshwater influx, is considerably much less saline than the southern basin. This salinity gradient contributes to the various vary of wildlife inhabiting the ocean. The Caspian Sea is famend for its wealthy biodiversity, together with quite a few species of fish, mammals, and birds. The sturgeon, notably prized for its caviar, is a flagship species of the Caspian Sea, although its populations have been drastically lowered as a result of overfishing and habitat degradation. Different notable inhabitants embrace seals, numerous varieties of fish essential for the native fishing trade, and a big selection of fowl species that make the most of the Caspian’s wetlands for breeding and migration.
Geological Historical past and Formation:
The Caspian Sea’s geological historical past is complicated and stretches again thousands and thousands of years. It’s believed to be a remnant of the Paratethys Sea, an enormous historic sea that existed throughout the Miocene epoch. Over time, tectonic actions and adjustments in sea ranges have formed its current kind. The ocean’s flooring is characterised by quite a lot of geological options, together with underwater mountains, plains, and canyons. The geological processes shaping the Caspian Sea proceed to this present day, influencing its hydrology and ecology.
Geopolitical Significance:
The Caspian Sea’s location on the intersection of Europe and Asia, and its proximity to important vitality reserves, has made it a area of appreciable geopolitical significance all through historical past. The 5 littoral states – Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan – all have competing pursuits within the sea’s assets and navigable waters. The division of the Caspian Sea’s assets, notably its oil and gasoline reserves, has been a topic of intense negotiations and agreements through the years. The 2018 Conference on the Authorized Standing of the Caspian Sea, signed by the 5 littoral states, represents a major milestone in resolving long-standing territorial disputes and establishing a framework for cooperation in useful resource administration and environmental safety.
Financial Significance:
The Caspian Sea is an important financial useful resource for the bordering nations. Its huge oil and gasoline reserves have made it a major vitality hub, attracting appreciable worldwide funding. Oil and gasoline extraction actions are prevalent within the Caspian Sea, contributing considerably to the economies of Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan. The fishing trade additionally performs an important position, although overfishing has threatened the sustainability of a number of key species. The Caspian Sea additionally helps different financial actions, together with transport and tourism. The event of port infrastructure and transportation networks alongside the Caspian coast is essential for facilitating commerce and financial growth within the area.
Environmental Challenges:
Regardless of its financial significance, the Caspian Sea faces important environmental challenges. Air pollution from industrial actions, oil spills, and agricultural runoff poses a severe risk to its ecosystem. Overfishing has depleted fish shares, notably sturgeon populations, with dire penalties for the area’s biodiversity and fishing trade. Local weather change can also be impacting the Caspian Sea, resulting in fluctuations in water ranges and altering its ecological stability. The introduction of invasive species has additional sophisticated the scenario, disrupting native ecosystems and creating competitors for assets. Worldwide cooperation and sustainable administration practices are essential to mitigate these environmental threats and make sure the long-term well being of the Caspian Sea.
Conclusion:
The Caspian Sea, a singular and huge inland physique of water, holds a major place on the world map, not solely geographically but in addition politically and economically. Its wealthy biodiversity, substantial vitality reserves, and sophisticated geopolitical dynamics make it a area of ongoing curiosity and concern. The challenges going through the Caspian Sea, notably these associated to environmental degradation and useful resource administration, require concerted worldwide efforts to make sure its long-term sustainability and the well-being of the communities that rely on it. The way forward for the Caspian Sea will rely on the power of the littoral states to stability financial growth with environmental safety, selling cooperation and sustainable administration practices to safeguard this distinctive and very important ecosystem for future generations.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into The Caspian Sea: A Landlocked Big on the World Map. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!