The Spinal Map: Unraveling the Complexities of the Spinal Wire
Associated Articles: The Spinal Map: Unraveling the Complexities of the Spinal Wire
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to The Spinal Map: Unraveling the Complexities of the Spinal Wire. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Spinal Map: Unraveling the Complexities of the Spinal Wire

The spinal twine, a seemingly easy cylindrical construction, is a marvel of organic engineering, appearing because the central communication freeway between the mind and the remainder of the physique. Understanding its intricate group, also known as the "spinal map," is essential for diagnosing and treating an enormous array of neurological circumstances. This map, removed from being a static illustration, is a dynamic interaction of sensory enter, motor output, and complicated interneuronal networks that govern reflexes, posture, and voluntary motion.
This text will delve into the intricacies of the spinal map, exploring its anatomical group, useful subdivisions, and the medical implications of understanding its complexities.
Anatomical Group: A Segmented Construction
The spinal twine, extending from the medulla oblongata to the conus medullaris (round L1-L2), just isn’t a homogenous construction. As an alternative, it is segmented, with every phase equivalent to a pair of spinal nerves. These segments, numbering 31 in complete (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal), are additional organized into grey matter and white matter.
The grey matter, formed like a butterfly or "H," is centrally situated and accommodates neuronal cell our bodies, dendrites, and axons of interneurons, motor neurons, and the receiving ends of sensory neurons. The grey matter is split into dorsal (posterior) horns, ventral (anterior) horns, and lateral horns (current solely within the thoracic and higher lumbar areas).
-
Dorsal horns: Obtain sensory data from the physique through the dorsal roots of spinal nerves. Totally different laminae (layers) throughout the dorsal horn course of several types of sensory data, comparable to contact, ache, temperature, and proprioception (sense of physique place).
-
Ventral horns: Include the cell our bodies of motor neurons, which ship alerts to skeletal muscle mass through the ventral roots of spinal nerves. The group of motor neurons throughout the ventral horn is somatotopically organized, that means that neurons innervating particular muscle teams are clustered collectively.
-
Lateral horns: Include the cell our bodies of preganglionic sympathetic neurons, that are concerned within the autonomic nervous system’s management of visceral features.
The white matter, surrounding the grey matter, consists primarily of myelinated axons that ascend and descend the spinal twine. These axons are organized into ascending tracts (carrying sensory data to the mind) and descending tracts (carrying motor instructions from the mind).
Practical Subdivisions: Tracts and Pathways
The spinal map is not nearly anatomical location; it is concerning the useful pathways that join completely different components of the nervous system. These pathways are essential for understanding how sensory data is processed and the way motor instructions are executed.
Ascending Tracts (Sensory):
-
Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscus Pathway: Carries details about tremendous contact, proprioception, and vibration. Axons ascend ipsilaterally (on the identical facet) within the dorsal columns earlier than crossing over within the brainstem.
-
Spinothalamic Tract: Carries details about ache, temperature, and crude contact. Axons cross over to the contralateral (reverse) facet of the spinal twine shortly after coming into.
-
Spinocerebellar Tracts: Carry proprioceptive data from the muscle mass and joints to the cerebellum, essential for coordination and stability. These tracts have each ipsilateral and contralateral parts.
Descending Tracts (Motor):
-
Corticospinal Tract (Pyramidal Tract): The foremost pathway for voluntary motor management. Axons originate within the motor cortex and descend, with most crossing over to the contralateral facet within the medulla.
-
Reticulospinal Tract: Concerned in regulating muscle tone, posture, and autonomic features.
-
Rubrospinal Tract: Contributes to motor management, significantly in higher limb actions.
-
Vestibulospinal Tract: Performs a vital function in sustaining stability and posture.
-
Tectospinal Tract: Concerned in orienting the pinnacle and eyes in response to visible and auditory stimuli.
Reflex Arcs: The Spinal Wire’s Autonomous Actions
The spinal twine does not merely relay data; it additionally performs a vital function in mediating reflexes – speedy, involuntary responses to stimuli. Reflex arcs contain sensory neurons, interneurons (usually throughout the grey matter), and motor neurons, making a closed loop that bypasses the mind for rapid motion. Examples embody the patellar reflex (knee-jerk reflex) and the withdrawal reflex (pulling your hand away from a scorching range). Understanding these reflex arcs is crucial for neurological examinations.
Medical Implications: Diagnosing Neurological Issues
The spinal map is essential for diagnosing a variety of neurological issues. Injury to particular areas of the spinal twine can result in attribute deficits, offering priceless clues concerning the location and extent of the damage.
-
Spinal Wire Harm: Trauma can lead to injury to ascending and descending tracts, resulting in sensory loss, paralysis, and different neurological deficits relying on the extent and severity of the damage.
-
A number of Sclerosis (MS): This autoimmune illness assaults the myelin sheath of axons within the central nervous system, resulting in quite a lot of neurological signs, together with weak spot, numbness, and imaginative and prescient issues. The placement of demyelination throughout the spinal twine can affect the precise signs skilled.
-
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): This progressive neurodegenerative illness impacts motor neurons, resulting in muscle weak spot, atrophy, and ultimately paralysis.
-
Syringomyelia: A fluid-filled cyst (syrinx) varieties throughout the spinal twine, compressing and damaging surrounding tissue. The signs rely upon the situation and measurement of the syrinx.
-
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA): A genetic dysfunction characterised by the degeneration of motor neurons within the spinal twine, resulting in progressive muscle weak spot and atrophy.
Neurological Examination and the Spinal Map
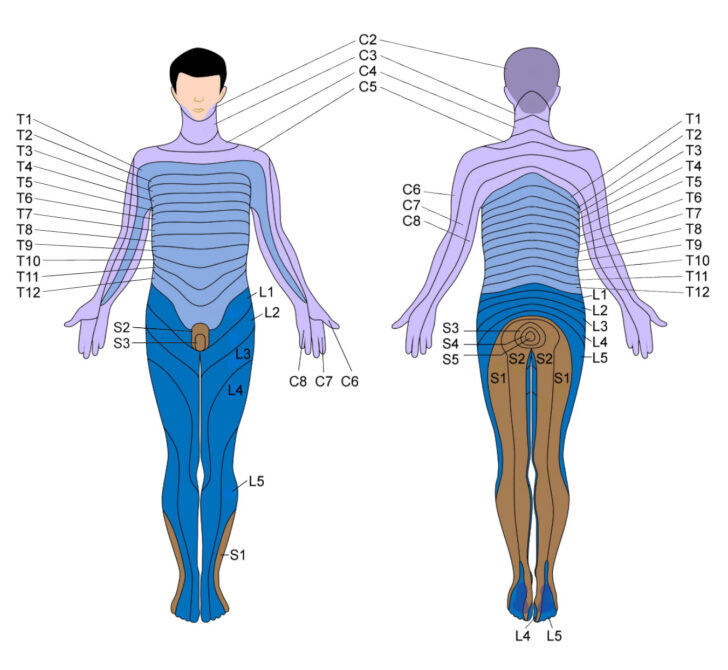
Neurological examinations rely closely on understanding the spinal map. Physicians assess sensory perform by testing contact, ache, temperature, and proprioception in numerous dermatomes (areas of pores and skin innervated by a single spinal nerve). Motor perform is evaluated by assessing muscle power, reflexes, and coordination. The sample of deficits can pinpoint the situation of the lesion throughout the spinal twine.
Superior Imaging Strategies:
Fashionable imaging methods, comparable to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans, present detailed photographs of the spinal twine, permitting for exact localization of lesions and evaluation of their extent. These methods are invaluable in diagnosing and managing spinal twine issues.
Conclusion:
The spinal map is a posh and dynamic system that performs an important function in coordinating sensory enter, motor output, and reflex exercise. Understanding its anatomical group and useful pathways is essential for diagnosing and treating a variety of neurological circumstances. As our understanding of the spinal twine continues to evolve, so too will our capacity to supply efficient and focused therapies for people affected by spinal twine issues. Additional analysis into the intricate interaction of neuronal circuits and the molecular mechanisms underlying spinal twine perform will undoubtedly result in new diagnostic instruments and therapeutic interventions sooner or later.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights into The Spinal Map: Unraveling the Complexities of the Spinal Wire. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!